
- South America
- Central & North America
- Europe & North/Central Asia
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- North Africa & the Middle East
- South Asia
South AmericaBush dog Speothos venaticus
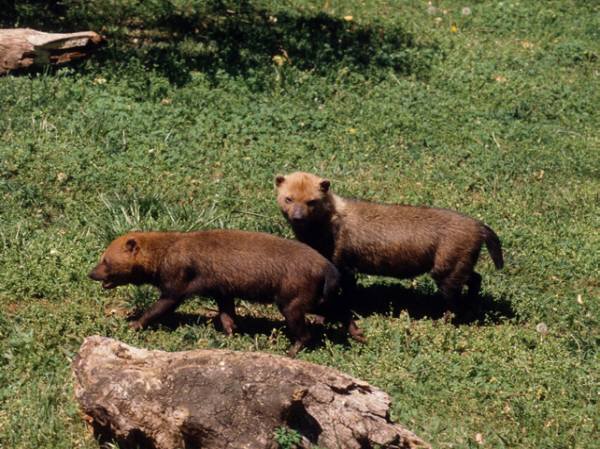

bush dog - © Gerald L Zuercher
Amazonian Canids Working Group - Karen DeMatteo and Fernanda Michalski are the coordinators of the Amazonian Canids Working Group. This working group is focused on four species: the short-eared dog, crab-eating fox, bush dog, and South American foxes. Amazonian canids are similar to many carnivores worldwide whose long-term survival is threatened by a variety of direct and indirect threats, including habitat loss, expansion of hydroelectric dams, illegal hunting of prey, and diseases from domestic dogs.
Projects- Proyecto Zorro Pitoco: Using noninvasive techniques to provide novel insights for the bush dogs and co-existing biodiversity in Misiones, Argentina
- Camera trap wildlife monitoring in and around Madidi National Park, Bolivia
- Investigation of neotropical helminthiasis and other parasites in the biotope of wild animals of the Misionera Forest, as potential foci of zoonoses
- Effect of climate change on carnivores in the Amazon
- Residents of the forest - canids from Amazon
- 2004 Status Survey & Convervation Action Plan - South America
- Why bush dogs are so different from other dogs
- Rare Amazon bush dogs caught on camera
- A rescue dog is now helping to save other (much wilder) dogs
- Amazing Species: bush dog
English: Bush Dog, Savannah Dog, Vinegar Dog
French: Chien Des Buissons, Zorro
Spanish; Castilian:Cachorro Vinagre, Guanfando, Pero Selvático, Perrito Venadero, Perrito de Monte , Perro De Monte, Perro Grullero , Perro Vinagre , Perro de Agua, Perro de la Selva, Umba, Zorrito Vinagre, Zorro Pitoco , Zorro Vinagre
German: Waldhund
Italian: Itticione, Speoto
Portuguese: Cachorrinho, Cachorro-do-mata, Cachorro-do-mato-cotó, Cachorro-do-mato-vinagre, Cachorro-pitoco
Justification
Although widespread, the Bush Dog appears to be rare over its entire range. The species has proven to be extremely difficult to locate in the wild, making estimates of population trends difficult. While one may expect a broadly distributed species with confirmed occurrences in fragmented or altered habitat to have a generally stable population, preliminary evidence from the field suggests that these areas may alter the Bush Dog’s ecological requirements resulting in an increase in the minimum area needed to support a group (and thereby putting the species at increased risk of either direct or indirect exposure to other threats). The species is here listed as Near Threatened based on an estimated decline of 20–25% in the past 12 years (estimated generation length = 4 years), thereby approximating the threshold for listing as Vulnerable under criterion A2. This decline is attributable to multiple threats, including ongoing habitat loss and fragmentation, reduction in prey abundance due to illegal hunting and predation by domestic dogs, and an increased risk from canid-related disease.
Geographic Range Information
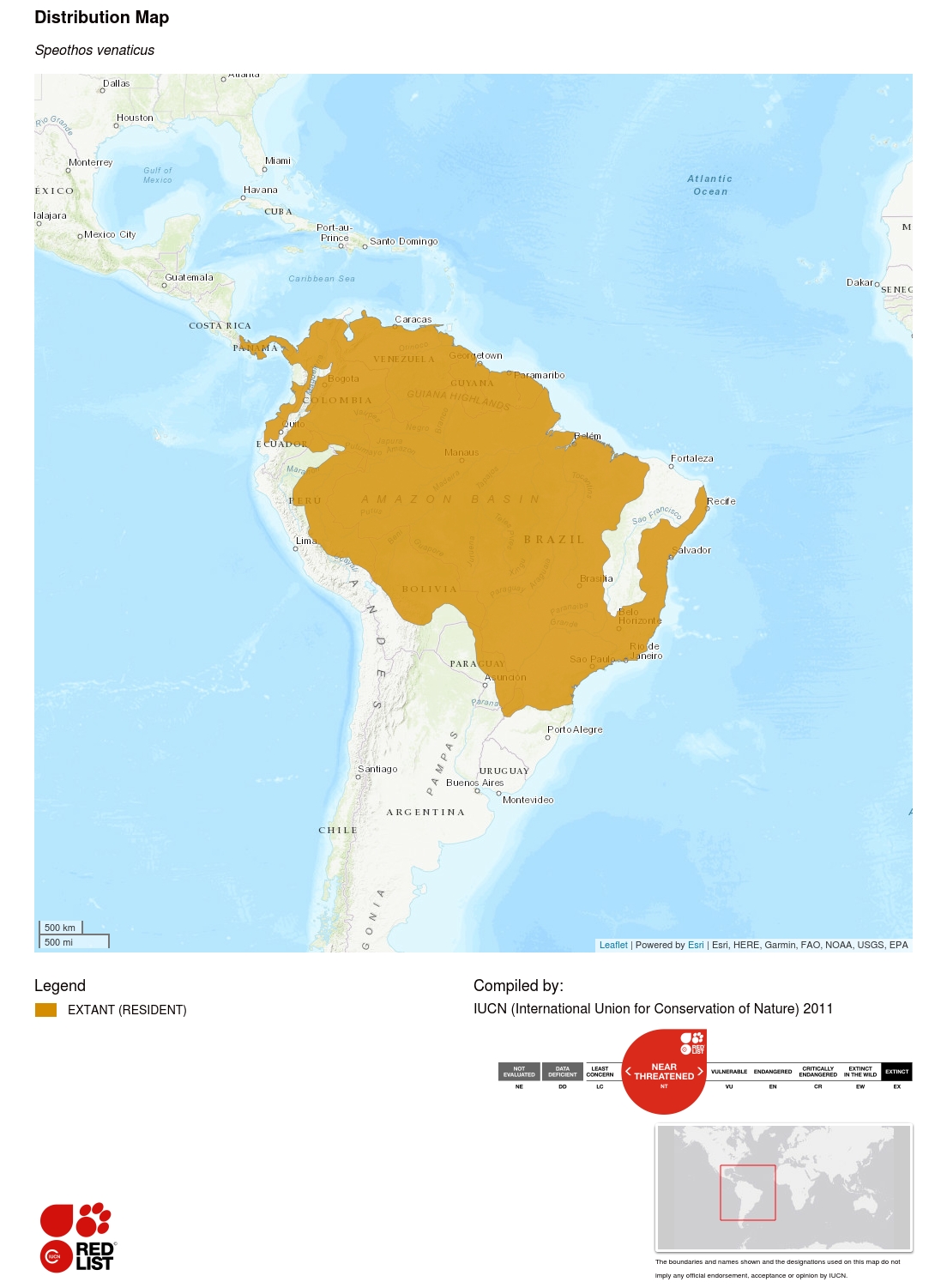
This species occurs from extreme eastern Central America and northern South America, south to Paraguay and north-eastern Argentina. Isolated subpopulations may also still occur in Ecuador and Colombia, west of the Andes. Its historical distribution may have extended as far north as Costa Rica (Rosa and Nocke 2002), where the species may still survive. The current distribution map was generated using the results of an extensive survey of carnivore biologists and literature for species presence (n = 399 historic locations), as well as a bioclimatic model predicting suitable area for the species (DeMatteo and Loiselle 2008). The latter authors estimated that the total area predicted to be suitable for Bush Dogs is in the order of 14,445,000 km², with 77% of this occurring within the current range.
Population trend:Decreasing
Population Information
Despite its large distributional range and occurrence in a variety of habitats, Bush Dogs seem to be naturally rare throughout their range. In a recent survey by DeMatteo (2008), the majority of countries in the Bush Dog’s distribution reported the status of the species as rare or unknown (rare: Ecuador; rare or unknown: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, French Guiana, Paraguay; unknown: Panama and Venezuela) and only two countries reported it as common (Guyana and Peru). The species is seldom recorded with camera traps; however, caution should be taken when interpreting the lack of detection, as this may actually be associated with the species actively avoiding features associated with this technique (e.g., placement of traps along animal trails used by other carnivores) or assumptions on animal movement (e.g., placement along roads assumes the animal will walk along the road versus cross over the road).
Demographic data for Bush Dogs are lacking throughout their range and population estimates have been reported only for a few areas: <100 in Misiones Argentina (DeMatteo 2008), >1,000 in Bolivia (DeMatteo 2008), > 1,000 in 4,022 km² or one individual/4 km² in Cusco Peru within the Camisea River region (DeMatteo 2008), 0.04 individuals/km² (B. Beisiegel pers. comm.) in Brazil, 0.025 individuals/km² in partially fragmented cerrado in Mato Grosso Brazil (E.S. Lima, K.E. DeMatteo, R.S.P. Jorge, M.L.S.P. Jorge, J. Dalponte, H.S. Lima, and S. Klorfine, pers. obs.), 15.8 individuals/394 km² or 0.04 individuals/km² in the Pantanal in Brazil (Lima, Jorge et al. 2009), and 0.001 individuals/km² in fragmented southern Amazonia Brazil (Michalski 2010). A suitable area of approximately 11,000,000km² (DeMatteo and Loiselle 2008), and an average population density of ca. 0.01 individuals/km², would predict an estimated population of 110,000 individuals, approximately half of which would be mature; however, the effects of fragmentation, degree of protection, and variability across their broad distribution would suggest that this is an over-estimate.
Across the Bush Dog’s distribution, population trends are reported as unknown in two countries (Guyana and Panama), declining in two (Paraguay and Venezuela), unknown or stable in one (French Guiana), and stable in two (Ecuador and Peru, specifically Cusco Peru) (DeMatteo 2008). Across the entire range, increasing levels of habitat fragmentation (urbanization and agriculture), threats to prey populations with illegal poaching, and exposure to potentially lethal candid-related diseases, mean that the probability that the trend is stable or increasing is highly unlikely.
Habitat and Ecology Information
Bush Dogs are reported to be a habitat generalist by indigenous peoples, within the context of occurring generally near water sources, particularly small streams, where prey densities may be higher (Zuercher et al. 2005; E.S. Lima, K.E. DeMatteo, R.S.P. Jorge, M.L.S.P. Jorge, J. Dalponte, H.S. Lima, and S. Klorfine pers. obs.; M. Swarner, pers. comm). Bush Dogs have been observed in lowland (below 1,500 m) forested habitats including primary and gallery forest (Defler 1986), semi-deciduous forest, and seasonally flooded forest (Aquino and Puertas 1997). Observations have also been recorded from cerrado habitat in Brazil (Silveira et al. 1998; Oliveira 2009, C. Brady pers. comm.) and Paraguay (Zuercher and Villalba 2002) and pampas (wet savanna) edge/riparian areas (Strahl et al. 1992, Emmons 1998). Recent reports mention Bush Dogs in three unique habitats: caatinga, chaco, and mangroves along the coast (DeMatteo and Loiselle 2008). In some cases, they have been observed several kilometers from forest habitat (Silveira et al. 1998). The species is also occasionally reported from secondary forest, ranchland (M. Swarner pers. comm.), fragmented cerrado ranchland (E.S. Lima, K.E. DeMatteo, R.S.P. Jorge, M.L.S.P. Jorge, J. Dalponte, H.S. Lima, and S. Klorfine pers. obs.; L. Silveira and A. Jácomo pers. comm.), disturbed areas (DeMatteo and Loiselle 2008, Oliveira 2009), and fragmented forest areas (Michalski and Peres 2005, Michalski 2010).
No habitat selection preference was found in either the Pantanal in Brazil (Lima, Jorge et al. 2009) or in the Upper Paraná Atlantic forest - cerrado mixture in Paraguay (Zuercher et al. 2005); however, some evidence has been found suggesting a preference for intact savanna and forest habitat versus altered (cropland and pastures) for a group of Bush Dogs in partially fragmented cerrado, indicating that habitat use and preference may differ by region and availability (E.S. Lima, K.E. DeMatteo, R.S.P. Jorge, M.L.S.P. Jorge, J. Dalponte, H.S. Lima, and S. Klorfine pers. obs.). While Michalski (2010) reported an absence of Bush Dogs in fragmented areas in southern Amazonia, others studies have demonstrated strong evidence that their occurrence is likely (DeMatteo and Loiselle 2008; Oliveira 2009; E.S. Lima, K.E. DeMatteo, R.S.P. Jorge, M.L.S.P. Jorge, J. Dalponte, H.S. Lima, and S. Klorfine pers. obs.); however, the intensity of use in these areas and impact on ecological requirements is unknown. Preliminary data from the field suggest that as the degree of habitat fragmentation increases so does the area required by Bush Dogs (E.S. Lima pers. comm.); while these data are only available for the cerrado ecosystem in Brazil, it is suspected to be true for all habitat types and a reflection of a negative relationship between prey density and habitat fragmentation. A reanalysis of the Bush Dog’s historical distribution (n > 250 locations) determined that approximately one-quarter (20%) were associated with fragmented/altered habitat and the percentage of modified habitat increased when the estimate was expanded from the area needed to support a single individual to the area to that of breeding group (DeMatteo and Loiselle 2008).
The reported variation in home range size estimates is likely associated with habitat integrity and prey density: 150 km² (Upper Paraná Atlantic Forest; Beisiegel 1999), ca. 16 km² (Beisiegel and Ades 2004), and 140 km² (Fixed Kernel 95%) for one group of Bush Dogs (n = 2–4 individuals) in cerrado (E.S. Lima, K.E. DeMatteo, R.S.P. Jorge, M.L.S.P. Jorge, J. Dalponte, H.S. Lima, and S. Klorfine, pers. obs.).
Preliminary field data supports captive studies that Bush Dogs exist in family groups with young from one or more litters (DeMatteo 2008, Michalski 2010, E.S. Lima, K.E. DeMatteo, R.S.P. Jorge, M.L.S.P. Jorge, J. Dalponte, H.S. Lima, and S. Klorfine, pers. obs.); however, solitary individuals are regularly observed in a variety of habitat types. Reproduction in the wild is aseasonal (DeMatteo 2008). The species appears to have a semi-nomadic movement pattern versus a true territory like many carnivores (DeMatteo 2008, E.S. Lima, K.E. DeMatteo, R.S.P. Jorge, M.L.S.P. Jorge, J. Dalponte, H.S. Lima, and S. Klorfine, pers. obs.) and has been recorded living in sympatry with Atelocynus microtis in Peru and Brazil (Leite Pitman, Beck et al. 2003, Michalski 2010). Estimated generation length is four years [(0.5 x reproductive length of six years) + sexual maturity at one year (in captivity; Porton et al. 1987).
Preliminary field data supports anecdotal reports of diet and the idea that Bush Dogs are highly carnivorous (Deutsch 1984, Peres 1991); however, there appears to be evidence of prey preference based on geographical region and habitat type, which is likely compounded by seasonal variability. For the Pantanal area in Brazil, the principal food item was Nine-banded Armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus; 94%) with small mammals, Agoutis (Dasyprocta azarae), and birds occurring in smaller quantities; however, no fruit was recorded (n = 17, identified by scent and tracks; Lima, Jorge et al. 2009). For the interior Atlantic forest in Paraguay, the majority of the diet was composed of Agoutis and Paca (Cuniculus paca) with small mammals, rodents, reptiles, invertebrates, and Cecropia fruit occurring in lower amounts (n = 11, identified using mitochondrial DNA; Zuercher et al. 2005). In a successful reproduction center in southeast Brazil, where meat and fruit (banana and papaya) are available, animals eat fruit and meat in equal proportions (L. Saboia, pers. comm.). Predation of poultry has been reported to occur occasionally (DeMatteo 2008).
Threats Information
There are several serious perceived threats, including: 1) human encroachment and loss of intact habitat due to large-scale agriculture (e.g., soybean), conversion of land to pasture, and large-scale plantations of monoculture trees (e.g., eucalyptus, pine); 2) reduction in prey abundance due to illegal poaching and domestic dog predation; and 3) increased risk of contracting lethal diseases from domestic dogs (proximity to human populations and hunting dogs (DeMatteo 2008).
Canid-related diseases are a threat not previously identified for Bush Dogs. However, field evidence supports that pathogens may be transmitted by domestic dogs, and the effects can be potentially devastating, mainly due to the species’ group living (Mann et al. 1980, Steinel et al. 2001, Leite Pitman, Nieto et al. 2003, Jorge, Morato et al. 2007, Jorge, Nunes, et al. 2007, DeMatteo 2008, Jorge et al. 2008, E.S. Lima, K.E. DeMatteo, R.S.P. Jorge, M.L.S.P. Jorge, J. Dalponte, H.S. Lima, and S. Klorfine, pers. obs.). E.S. Lima, K.E. DeMatteo, R.S.P. Jorge, M.L.S.P. Jorge, J. Dalponte, H.S. Lima, and S. Klorfine (pers. obs.) observed this effect when a generalized hair loss, suspected to be a type of mange, gradually spread through a group of wild Bush Dogs, eventually killing all individuals. In addition to mange, parvovirus and rabies are diseases reported as negatively effecting wild populations (Mann et al. 1980, DeMatteo 2008). The species has been identified to be susceptible to both Dioctophyma renale and Amphimerus interruptus (museum collections - Vierira et al. 2008), Lagochilascaris sp. (Volcán and Medrano 1991), and as a host for Echinococcus vogeli (Cestoda: Taeniidae) (Rausch and Bernstein 1972). Captive animals have been identified as susceptible to a variety of diseases and parasites, including parvovirus (Janssen et al. 1982), vaccine-induced canine distemper (McInnes et al. 1992), leishmania (Lima, Fattori et al. 2009), Spirocerca lupi (Rinas et al. 2009), Toxoplasma gondii (Sedlak and Bartova 2006), and Campylobacter (L. Saboia pers. comm.). With the latter, 13 of 15 individuals in a large family group suddenly died from severe haemorrhagic enteritis when they contracted Campylobacter from an infected Coati that they were inadvertently fed (L. Saboia pers. comm.). This loss of multiple animals in a short period emphasizes both the species sensitivity to various diseases and the susceptibility of group living species to pathogens. With increasing proximity to human areas and intrusion into protected areas with hunting dogs, the risk of exposure to disease is potentially high. Exposure to disease may also result from feral or semi-feral, non-vaccinated, domestic dogs that regularly hunt prey independent of humans (K. DeMatteo pers. obs.). DeMatteo (2008) noted that in Brazil more problem interactions were noted to occur between Bush Dogs and domestic dogs than with livestock, which only emphasizes the threat of disease to the species.
Use and Trade Information
Bush dogs have been reported shot in five countries (Argentina, Brazil, Panama, Peru, Venezuela) and trapped in two (Panama and Peru) (DeMatteo 2008, F. Michalski unpubl. data). In Peru, these events were associated with natives reporting that they will eat Bush Dogs if snared or if they have the rare opportunity to collect then with traditional hunting; however, Venezuela reported shootings were associated with the occasional collection of trophies due to its rarity (DeMatteo 2008).
Conservation Actions Information
This species occurs in several protected areas throughout its range, but it has a patchy distribution and occurs at very low densities. Hunting is prohibited in Colombia (Law Number 848:1973), Ecuador (Law Number 74:1981), French Guiana (Law Number JO19860625:1986), Panama (Law Number 2-80:1980), Paraguay (Law Number 18796:1975) and Peru (Law Number 5056:1970). Hunting and trade is regulated in Argentina (Law Number 22.421:1981), Bolivia (Law Number 12301:1975), Brazil (Law Number 5197:191967), and Venezuela (Law Number 276:1970). There is no Information for Guyana and Suriname. Unfortunately, in many parts of its range, resources are inadequate to manage designated protected areas and enforce existing wildlife laws.
Included in CITES on Appendix I.
Bush Dogs occur in captivity and are part of a successful international breeding programme (Buck 2009), which includes Asia (Japan), Europe, Brazil, and North America. There have been no known attempts at reintroduction.
Population estimates and demographic data for Bush Dogs is still little known across its range. This extends to an understanding of the social dynamics of individual groups, especially in terms of dispersal of young and area of use relative to other groups (overlapping or separate home ranges). Habitat associations are not clearly understood – the species was once thought to be dependent on forests but is now increasingly observed in open and fragmented habitats; however there is no data on population viability in such areas. While preliminary data on diet supports a primarily carnivorous diet, seasonal changes and geographical variation in diet needs to be evaluated. Determining how the impact of disease, especially transmission dynamics from domestic dogs, can be managed or minimized in wild populations needs to be addressed. Interspecific relationships with sympatric carnivores needs to be further evaluated.
Locating evidence of species presence using standard survey techniques, including camera traps and transect surveys, has proven difficult (Beisiegel 2009, DeMatteo et al. 2009, Michalski 2010). The use of artificial scent lures, which can increase attraction to a specific location, have been unsuccessful with wild Bush Dogs (Zuercher et al. 1999). However, there are several methodological adjustments that may increase the effectiveness of these techniques with the species, including adjusting the height of camera placement, increasing trapping effort, and concurrent use of long-call vocalization playbacks and conspecific urine (DeMatteo et al. 2004). Limited field trials in partially fragmented cerrado (2004-2005) with playbacks, urine, and leg-hold traps were unsuccessful (K. DeMatteo unpubl. data). However, additional trials are needed to determine how species density, habitat variability (forest versus cerrado), and prey density alters technique effectiveness.
Preliminary and ongoing research using a combination of three non-invasive techniques (scent-detection dogs, faecal DNA screening, GIS technology) has been shown to be successful for the species (DeMatteo et al. 2009, unpubl. data) and should be expanded to additional regions and habitat. This suite of techniques eliminates the need to attract the species to a specific location and allows insight into many ecological variables including habitat use (intact and fragmented), population status, minimum area of use, and niche overlap/separation with other carnivores.

